List types of Controllers?
- PID
- Microcontroller: a computer implemented on a single chip, can be programmed, not expensive but sensitive to noise, and can't be used in industrial apps.
- PLC
- DCS
- SCADA
What are DCS, and DCS components?
Distributed systems connected by network for communications and monitoring.
DCS Componets
- Feild Control System
- Enginerring Station: for I/O configuration
- Opertor station: for monitoring
What are SCADA, and SCADA components?
Highly distributed system used to control geographically scattered assets over thousands of square kilometers. Used to collect data and send alarms.
SCADA component:
- Human Machine Interface (HMI) : for monitoring
- Supervisory (computer) system: gathers process data and sends commands to the process.
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) : converting sensor signals, sending to the supervisory system
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLCs)
- Communication infrastructure: provides connectivity
What is meant by PLC?
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a digital computer used for control; it replaced traditional relays due to their flexibility and reliability.
Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- The "brain" of the PLC.
- Executes the user program and controls the overall operation.
- Processes input signals and generates output signals.
- Manages system memory and communication with other devices.
Input Modules:
- Receive signals from sensors, switches, and other input devices.
- Convert physical signals (e.g., voltage, current) into digital signals.
- Transmit the digital signals to the CPU for processing.
Output Modules:
- Receive signals from the CPU.
- Convert digital signals into physical signals (e.g., voltage, current).
- Drive actuators, motors, solenoids, and other output devices.
Power Supply:
- Provides the necessary power to the PLC and its components.
- Ensures stable operation even in harsh industrial environments.
Memory:
- Stores the user program, system data, and configuration settings.
- Types of memory:
- Program memory: Stores the user-defined program logic.
- Data memory: Stores temporary and permanent data.
- System memory: Stores system configuration and diagnostic information.
- Program memory: Stores the user-defined program logic.
Communication Interfaces:
- Enable communication with other PLCs, computers, and network devices.
- Common interfaces:
- Serial ports (RS-232, RS-485)
- Ethernet
- Fieldbus (PROFIBUS, CANopen)
- Serial ports (RS-232, RS-485)
- Fixed Input/Output: Low cost, does not support extensions.
- Modular: can expand by including new unit (extension)
- Rack: expensive; supports 256 input and 256 output.
- Signal Modules: For input/output modules (Digital Input, Digital Output, Analog Input, and analog output)
- Function Modules (FM): (High speed counter, Temperature control,...)
- Communication Processor (CP): for the networking communication
- Memory Size
- CPU Speed/Speed of execution
- Network capabilities
- Max no. of input
- Max no. of output
- Type of input (Digital/Analog)
- Type of output(Digital/Analog)
- Cost
- Manufacture
- Vendor
- Accuracy
- Resolution
- Repeatability
- Range
- Linearity
- Response Time
- Cost
- Environment
- Ladder Logic (LD)
- Function Block Diagram (FBD)
- Structured Text (ST)
- Instruction List (IL)
- Squential Function Chart
- Flow Charts
|
PLC |
PC |
|
Programmable
Logic Control |
Personal
Computer |
|
Optimized for
single task |
Optimized for
multitasks |
|
Used in industrial
environment for Control tasks |
Used for personal
tasks |
|
Can operate
in High temperature |
Can’t operate
in High temperature |
- DC, One Phase AC motors need relays to start/stop.
- AC 3 Phase motor needs condactor.
- For a DC motor, just change positive and negative to change the motor direction.
- For AC 3 Phase: just change the power source between two phases
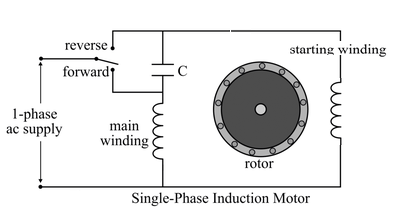
- For AC 1 Phase: Make the capacitor in series or in parallel with main coil to change the direction.
- For a DC motor: increase volt and give power as pulses to avoid increasing Ampear (using pulse width modulation)
- For AC 1/3 Phase: increase AC frquancy.
- S-On Delay Timer (S-ODT): Dealy output with TV value
- S-Off Delay Timer (S-OffDT): Output start directly with input and continues after input with TV value
- S-Pulse Extent Timer (S-PEXE): when get input signal a pluse with TV widths will out
- S: Input Signal
- TV: Time Value ==> S5t#10s
- Q: Output Signl
- S-CU: Counter up with no limits, need comparetor to catch the required value.
- S-CD: Counter Down From PV to Zero, needs two SET, One when start and Second when Done.
- S-CUD: Counter Up/Down, CU increase CV, CD descrease CV.
- Q: Give outputs when CV>0
- CV: Counter Value ==> C#50
- S: Set CV with PV value
- R: Reset all to zeros
- PV: Preset Value
List Comparators Types (CMP)?
- Integer: One Word
- Double: Two Words
- Float: Two Words
- >
- >=
- <
- <=
- =
- !=












No comments:
Post a Comment